Once testing is over, the OnlineIPT instantly generates an oral score report and a student diagnostic report. These PDF files are stored on the system and can be e-mailed to a teacher or school administrator as needed. The OnlineIPT individual diagnostic report not only includes the proficiency level designation, but also includes rich detailed diagnostics that can help the teacher inform instruction.
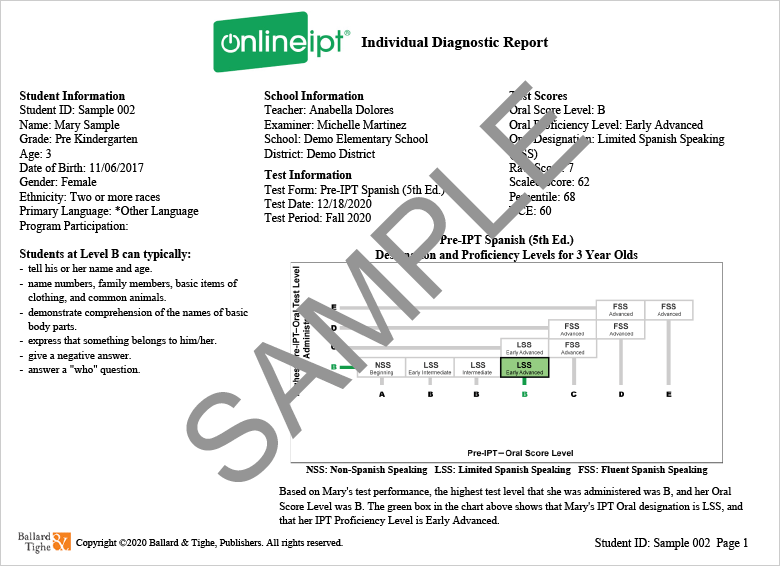
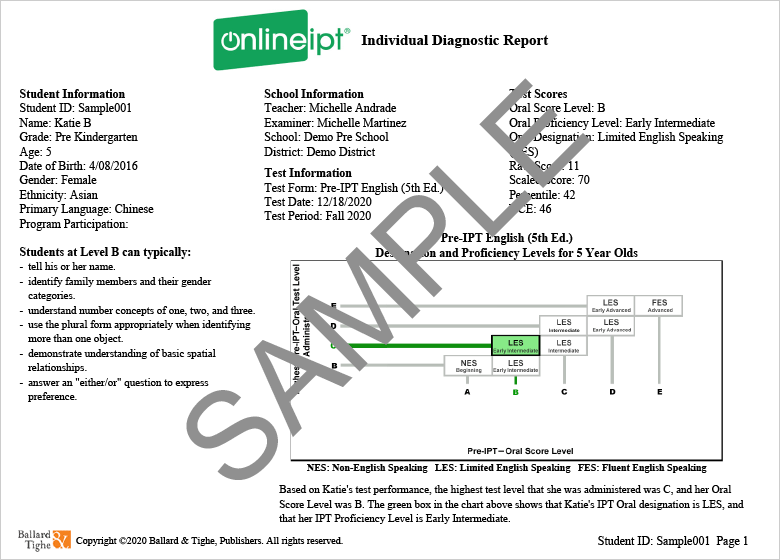
The results of the OnlineIPT Oral Tests are reported as an Oral Score level, as one of three designations: Non-, Limited, or Fluent English Speaking (NES, LES, FES) for the English tests and Non-, Limited, or Fluent Spanish Speaking (NSS, LSS, FSS) for the Spanish tests, and as one of five proficiency levels (Beginning, Early Intermediate, Intermediate, Early Advanced, and Advanced). These scores are based on the test level (A–E) that the student achieved on the basis of the stopping rules during test administration.
When the IPT is used for initial identification, these scores are used for designating the student as an English Learner or Spanish learner, or as English or Spanish proficient. When the IPT is used for other purposes such as progress monitoring or program exit, the proficiency level and designation scores may also be used to compare the student’s scores against his or her previous scores or against program exit requirements.
The OnlineIPT also provides group summary reports at the teacher, school, and district levels. These reports show how a group of students is distributed across the proficiency levels. Access to sample reports and options for running your own reports are provided on the Reports tab on the OnlineIPT.
The OnlineIPT also provides another set of score data based on the number of items that the student answered correctly during test administration, which is known as the student’s raw score. The raw score can be reported in standardized score units: scaled scores, percentiles, and normal curve equivalents (NCEs). All these scores are presented in list form in the top right hand portion of the first page of the student’s diagnostic score report, and it is also included in each student’s Oral Score Report.
To see a sample of the Spanish Diagnostic Report, click here
Oral Score Level
The Oral Score Level is a criterion-referenced score. The Pre-IPT test items are organized into sets (B–E), from simple to complex, that represent skills typical for language learners at different proficiency levels. Each student's Oral Score Level indicates the highest difficulty level on the test that the student performed on successfully. You can see the skills coverage of the IPT Oral test levels by looking at the columns in the record of student answers on page 2 of the Individual Diagnostic Report.
Oral Designation
The Oral Designation categories are called Non-English Speaking (NES), Limited English Speaking (LES), and Fluent English Speaking (FES) for the English tests and Non-Spanish Speaking (NSS), Limited Spanish Speaking (LSS), and Fluent Spanish Speaking (FSS) for the Spanish tests. Although referenced to the level of language skills shown on the test, the designation categories are norm-referenced and age-specific in the sense that as students advance in age, more language skills are expected of them to achieve a Limited or a Fluent designation than from younger students.
Oral Proficiency Level
The IPT Oral Proficiency Levels are Beginning, Early Intermediate, Intermediate, Early Advanced, and Advanced, and they correspond to the proficiency levels used in Ballard & Tighe’s instructional product lines. These score categories were developed to provide greater detail on the student’s oral proficiency within the “Limited” designation: The Beginning level corresponds to the Non-designation category, the Early Intermediate, Intermediate, and Early Advanced levels correspond to the Limited designation, and the Advanced level corresponds to the Fluent designation. Similarly to the designation categories, the proficiency levels are both criterion- and norm-referenced and grade-specific.
Raw Score
The Raw Score is the number of items the student answered correctly during the test administration. If any test levels are not administered because the rules for test starting level were applied, all items in the early test levels are assumed to be answered correctly. If any test levels are not administered as a result of applying the stopping rules in the course of the test, the items in the test levels above the one where testing was stopped are assumed to be answered incorrectly.
Scaled Score
The scaled score is a translation of a student’s raw score onto a common scale that has the same meaning for all the IPT Oral English tests. A common scale is useful for making comparisons across different forms and levels. Once a raw score has been converted to a scaled score, it may be compared to scaled scores from a different form (for example, a scaled score from Form G may be compared to a scaled score on Form H). Additionally, a scaled score may be compared to scaled scores from other levels, such that changes in performance can be studied across time. The scaled scores are on a continuous vertical scale that links together the IPT Oral English Tests (Pre, I, and II) and allows growth to be determined across levels. The scaled scores were derived using Rasch models. The forms were equated using equipercentile equating, where percentiles were compared for participants taking the same test levels. The scale was linked using the median Rasch scores of same-age students taking two different tests. Scaled scores are useful for tracking student progress via score gains.
Percentile Rank
The Percentile Rank ranges from 0 to 100, with 50 indicating median (average) performance for grade-specific groups of students in the norming sample. Raw scores below the lowest observed score in the sample have a percentile of 0, while raw scores above the highest observed score in the sample have a percentile of 100. For example, if a student who is tested in 7th grade achieves a percentile score of 50, it means that 50% of the students in the grades 6–8 norming sample scored at or below that score. The decision to group students from grades 6, 7, and 8 together in the norming analyses was based on the similarity of the score distributions for these students’ scores compared with students from grades 9-12. Percentiles must be interpreted relative to the group from which they were derived, i.e., the norming subsample.
NCE
NCE stands for Normal Curve Equivalent score. This score is derived from percentile ranks and is typically used for research. The NCE scale, like percentiles, ranges from 0 to 100, and it has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 21.06. Unlike percentiles, NCEs represent an equal interval scale and should be used instead of percentiles when averaging scores or computing gains over time within a single IPT Oral test level, e.g. the Pre-IPT.
Copyright © 2021 Ballard & Tighe, Publishers, a division of Educational Ideas, Inc.
These pages may be printed for use by course participants only.